Abstract
Serverless promised instant scaling but delivered cold starts—the latency penalty when a new function instance spins up. For real-time validation, API gateways, and user-facing interactions, Python's 200-500ms cold start is a UX killer. Rust eliminates this tax with 10-50ms cold starts, 10x faster execution, and 10x lower costs. This paper examines when and how to make the switch.
1. The Hidden Tax on Every Request
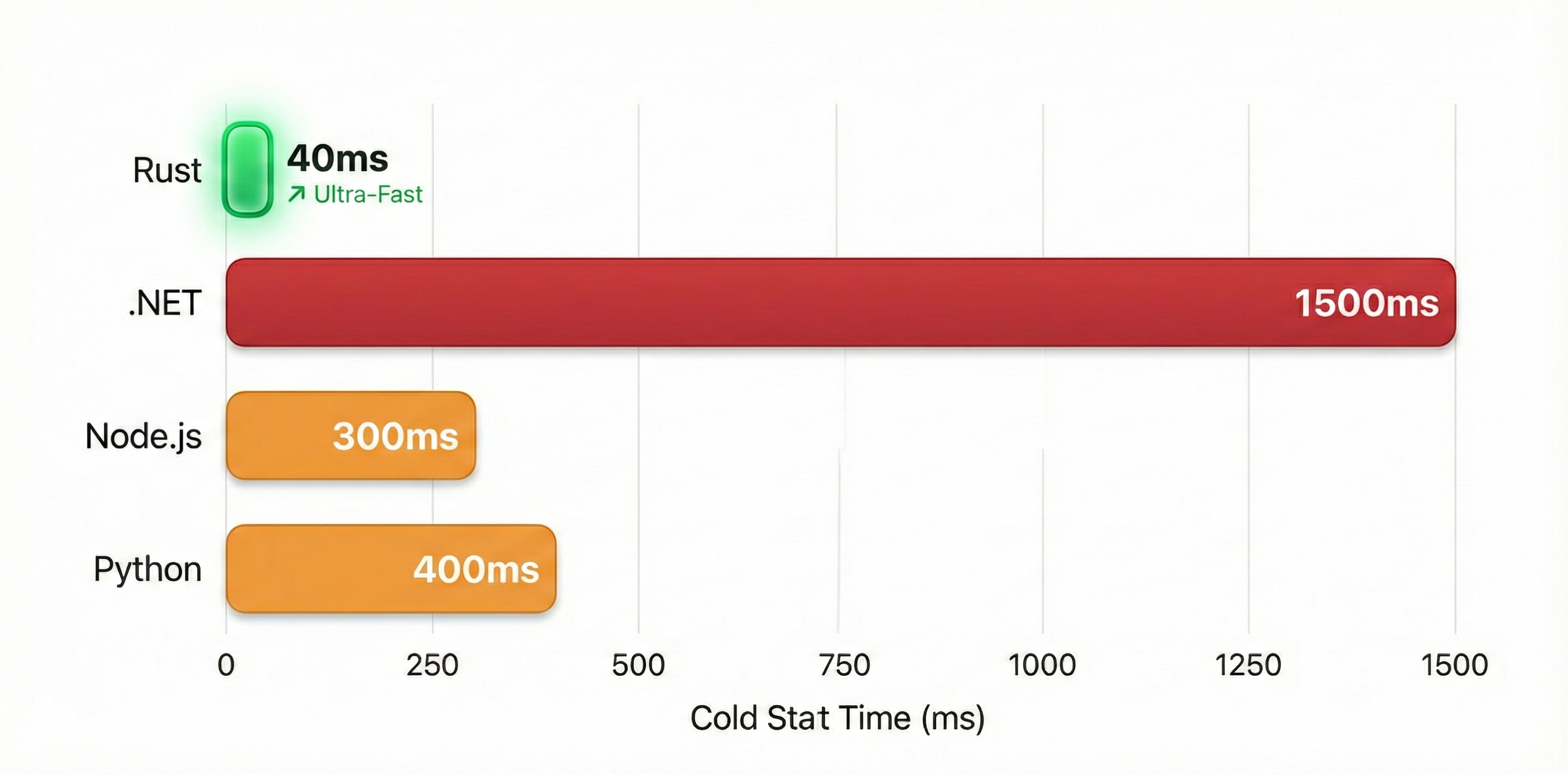
Serverless promised instant scaling. What it delivered was cold starts—the latency penalty when a new function instance spins up. For most applications, this is acceptable. For real-time validation, API gateways, and user-facing interactions, it's a UX killer.
| Language | Cold Start | Warm Start | The Gap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python | 200-500ms | 20-100ms | 180-400ms penalty |
| Node.js | 150-400ms | 10-50ms | 140-350ms penalty |
| .NET (pre-AOT) | 800-3000ms | 50-200ms | 750-2800ms penalty |
| Rust | 10-50ms | 1-5ms | 9-45ms penalty |
When your validation runs on every keystroke, that 400ms Python cold start isn't an edge case—it's the experience for the first user of every scaled instance.
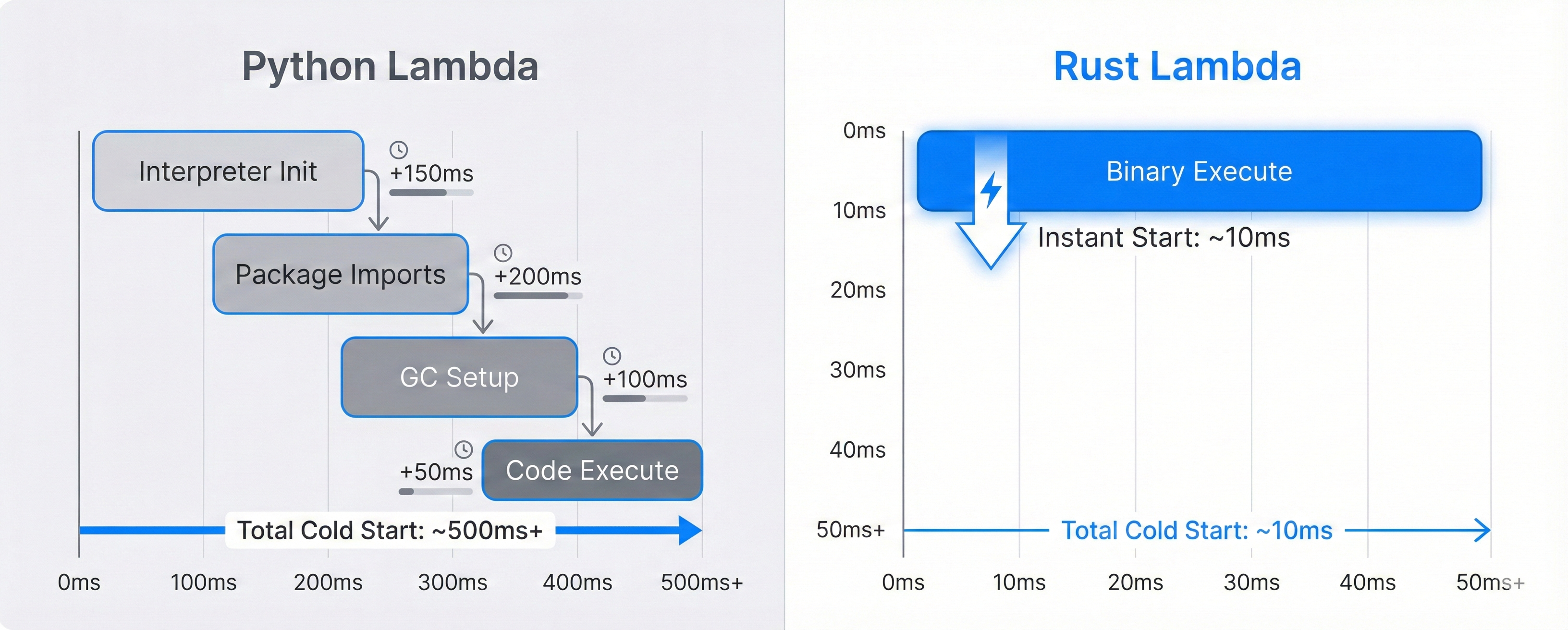
2. Why Python is Slow to Start
Python's cold start includes multiple initialization steps that compound:
- Runtime initialization — The Python interpreter must load
- Package imports — Every
importexecutes code - Dependency trees — NumPy, Pandas, etc. have deep initialization
- Garbage collector setup — Memory management overhead
Even "optimized" Python with stripped dependencies hits 150-200ms minimum.
3. Why Rust Starts Instantly
Rust compiles to a native binary. There's no runtime to initialize:
- No interpreter — Machine code executes directly
- No imports — Dependencies compiled into binary
- No GC — Memory managed at compile time
- Minimal bootstrap — Just load and run
A Rust Lambda is functionally identical to a C program in startup characteristics, with modern language safety.
The Core Insight
Rust doesn't have a "fast cold start." Rust barely has a cold start at all. The 10-50ms you see is primarily AWS container initialization, not language overhead.
4. Real-World Impact
Scenario: Validation on Form Submission
User fills out a form. Submits. Validation runs.
| Language | Cold Start Chance (5% traffic) | P95 Latency |
|---|---|---|
| Python | 1 in 20 users | 450ms |
| Rust | 1 in 20 users | 55ms |
That 1-in-20 user with Python gets a half-second delay. With Rust, they don't notice.
Scenario: API Gateway at Scale
1000 requests/second, auto-scaling from 10 to 50 instances during spike:
| Language | New Instances | Cold Start Delay | User Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python | 40 | 400ms each | 4% of requests delayed |
| Rust | 40 | 40ms each | Imperceptible |
5. The Cost Multiplier
Lambda bills by execution time (rounded to 1ms). Faster execution = lower cost.
| Language | Avg Execution | Monthly Cost (1M invocations) |
|---|---|---|
| Python | 150ms | $2.50 |
| Rust | 15ms | $0.25 |
Faster execution means lower costs. The actual savings depend on your workload profile—CPU-bound tasks see the biggest gains, while I/O-bound tasks may see less dramatic improvement since network latency dominates.
6. When Python Still Wins
Rust isn't always the answer:
- Data science workloads — NumPy/Pandas ecosystem unmatched
- Rapid prototyping — Python is faster to write
- ML model inference — Python bindings to TensorFlow/PyTorch
- Batch processing — Cold start irrelevant for long-running jobs
When Rust Wins
Real-Time APIs
Every millisecond matters for user experience
User-Facing Validation
Runs on every interaction, can't afford cold starts
High-Frequency Lambda
Many short invocations where startup dominates
Cost-Sensitive Workloads
Execution time is money at scale
7. The Migration Path
You don't rewrite everything. You identify the hot path:
- Profile your Lambda fleet — Find functions with high invocation + latency sensitivity
- Extract the core logic — The CPU-bound validation, not the I/O
- Rewrite in Rust — Using
cargo-lambdafor AWS integration - Keep Python for orchestration — If needed, Python calls Rust microservices
Production Considerations
| Rust Advantages | Rust Challenges |
|---|---|
| Memory safety without GC | Steeper learning curve |
| Fearless concurrency | Longer compile times |
| Predictable performance (no GC pauses) | Smaller ecosystem for some domains |
| Small binary size | Fewer developers available |
8. Conclusion
For serverless functions where latency matters, Rust eliminates the cold start tax that Python users have accepted as inevitable.
It's not about Rust being "better." It's about Rust being better for this use case—real-time, user-facing, latency-sensitive workloads where every millisecond of cold start is a UX regression.
References
- AWS Lambda Execution Environment — AWS documentation on Lambda lifecycle
- Rust Runtime for AWS Lambda — AWS blog on Rust Lambda performance
Want to know more about Rust for serverless? Contact me, I'm always happy to chat!
